NSAIDs for Swelling: How They Work and What to Watch For
When dealing with NSAIDs for swelling, non‑steroidal anti‑inflammatory drugs that target pain and fluid buildup in injured tissues. Also known as pain‑relieving anti‑inflammatories, they form a core part of everyday medicine.
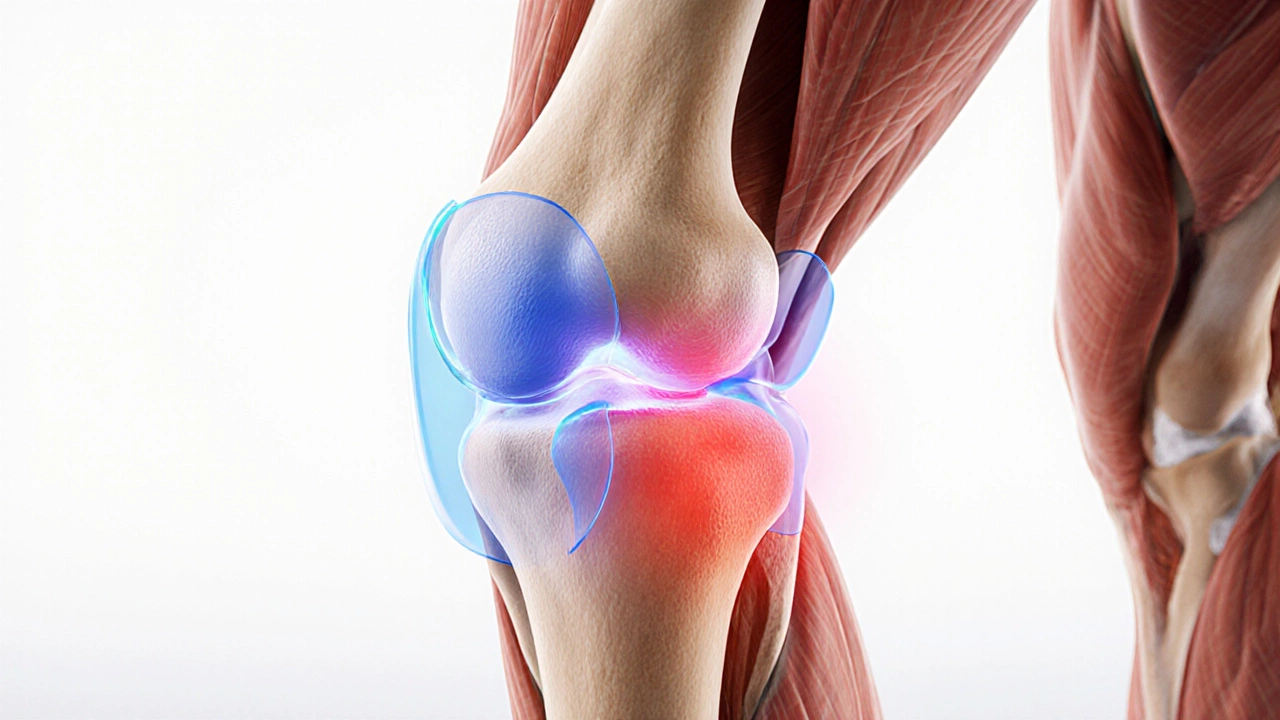
NSAIDs for swelling are a broad class, but the idea behind them is simple: they block enzymes that drive COX enzymes, cyclo‑oxygenase proteins that create prostaglandins, the chemicals that cause pain and swelling. By turning down prostaglandin production, the drugs calm the body’s alarm system and let you move more comfortably. This mechanism links directly to inflammation, the natural response that brings heat, redness, and swelling to protect damaged tissue. When inflammation spikes, swelling follows, and the NSAID steps in to break that chain.
Common Options and How to Choose
Most people recognize ibuprofen, a widely available NSAID that comes in 200 mg tablets and works well for mild to moderate swelling. Naproxen, diclofenac, and aspirin are other choices, each with slightly different dosing schedules and strength. For example, ibuprofen is typically taken every 6‑8 hours, while naproxen can last up to 12 hours, meaning fewer pills but a higher individual dose. Picking the right drug depends on the injury’s severity, how quickly you need relief, and any existing health conditions.
While NSAIDs are effective, they aren’t risk‑free. The same side effects, gastrointestinal irritation, kidney strain, and increased heart risk that can appear with long‑term use make it essential to follow dosage guidelines and talk to a doctor if you have ulcers, kidney disease, or heart problems. In many cases, alternating NSAIDs with acetaminophen or using topical gels can lower systemic exposure while still easing swelling.
Understanding the link between inflammation, COX inhibition, and the specific drug you pick lets you use NSAIDs safely and get the most out of them. Below you’ll find articles that dive deeper into dosage charts, herbal alternatives, and what to do if you experience common side effects, giving you a practical toolkit for managing swelling without compromising overall health.